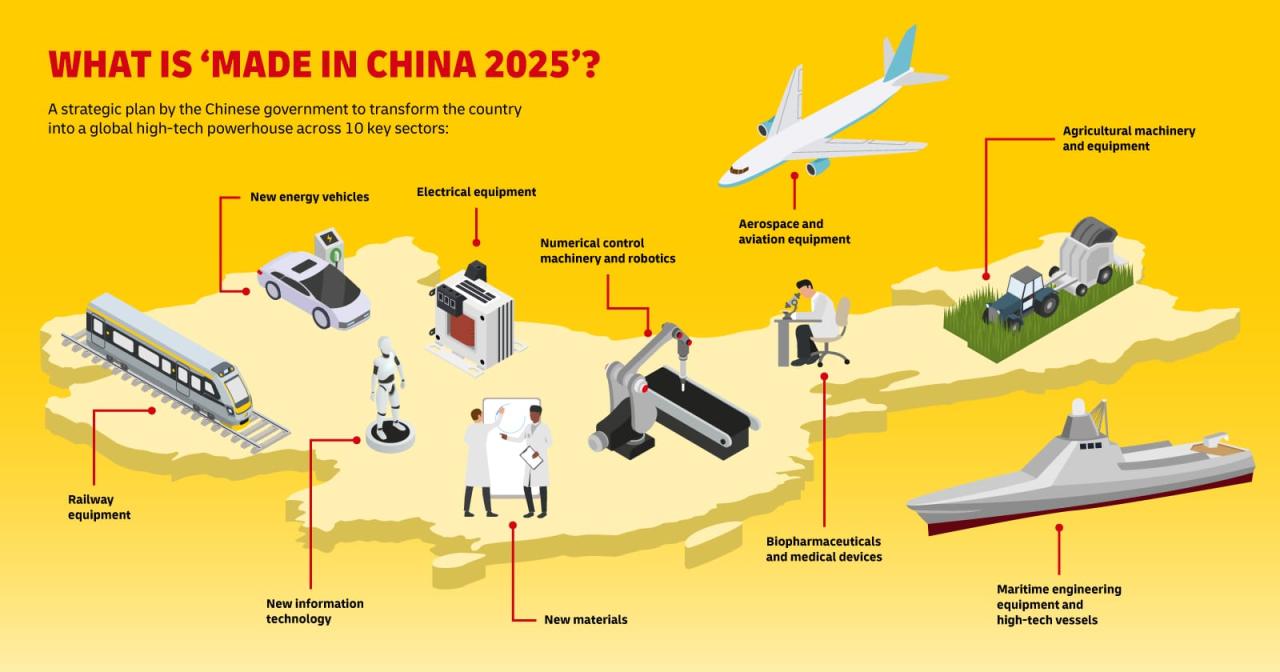
China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News. This statement, while seemingly straightforward, reveals a complex story of economic growth, strategic planning, and global impact. We’ll explore how China rose to become the world’s factory, examining the factors behind its success, the challenges it faces, and the ripple effects felt across the globe.
From its humble beginnings to its current dominance, China’s manufacturing sector has undergone a remarkable transformation. This journey involved significant investments in infrastructure, strategic government policies, and the harnessing of a vast workforce. But this rise hasn’t been without its hurdles; rising labor costs, technological competition, and geopolitical tensions all pose significant challenges for the future.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance
China’s rise as the world’s manufacturing powerhouse is a remarkable story of economic transformation. From a largely agrarian economy, it has evolved into a global manufacturing giant, impacting global trade, supply chains, and geopolitical dynamics. This exploration delves into the historical context, contributing factors, challenges, and global implications of China’s manufacturing hegemony.
China’s Manufacturing Evolution
China’s manufacturing sector’s growth is a multi-decade journey marked by strategic policy shifts and significant investment. It began with gradual opening-up and export-oriented industrialization, accelerating significantly after joining the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2001.
Key milestones include the establishment of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) in the late 1970s, attracting foreign investment and fostering export-driven growth. Subsequent infrastructure development, including transportation networks and energy grids, further fueled expansion. Specific industries where China achieved dominance include textiles, electronics, toys, and more recently, high-tech manufacturing components.
| Country | 1993 | 2003 | 2013 | 2023 (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | $300B | $1T | $3T | $5T+ |
| USA | $1T | $1.5T | $2T | $2.5T |
| Germany | $400B | $600B | $800B | $1T |
| Japan | $700B | $800B | $900B | $800B |
Note: Figures are approximate and represent manufacturing output in USD. Data variability across sources necessitates broad estimations.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – a huge part of that involves complex supply chains. To manage those effectively, you often need someone with broad technical skills, like a full stack developer , who can handle everything from databases to user interfaces. Understanding these technological underpinnings is crucial to grasping the full scope of China’s manufacturing superpower status.
Factors Driving China’s Manufacturing Success
Several interconnected factors propelled China’s manufacturing dominance. Low labor costs, initially a significant advantage, attracted substantial foreign direct investment (FDI). Massive infrastructure development, including improved transportation networks and reliable energy supply, facilitated efficient production and distribution. Government policies, such as tax incentives and export subsidies, actively promoted industrial growth.
Compared to other manufacturing hubs, China offered a unique combination of scale, cost-effectiveness, and government support. While other countries might excel in specific niche areas, China’s comprehensive manufacturing ecosystem, encompassing a vast supply chain and skilled workforce, provided a distinct competitive edge.
So, the Hacker News thread on China’s manufacturing dominance is fascinating. It got me thinking about global supply chains and how a single injury, like Bumrah’s back spasms, as reported here: Bumrah leaves SCG for scans after experiencing back spasms , can disrupt even the most finely tuned systems. This highlights how interconnected everything is, even when comparing the massive scale of Chinese manufacturing with the individual impact of a sports injury.
It makes you appreciate the fragility of global systems, doesn’t it?
Challenges and the Future of Chinese Manufacturing, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News

Despite its current dominance, China’s manufacturing sector faces emerging challenges. Rising labor costs, particularly in coastal regions, are impacting profitability. Technological advancements, especially in automation and artificial intelligence (AI), necessitate adaptation and potential job displacement in certain sectors. Trade wars and geopolitical tensions introduce uncertainty and potentially disrupt established supply chains.
- Investing heavily in automation and AI to maintain competitiveness.
- Focusing on higher-value-added manufacturing and technological innovation.
- Developing a more sustainable and environmentally friendly manufacturing sector.
- Strengthening domestic consumption to reduce reliance on exports.
- Improving intellectual property protection to attract more advanced technology.
Global Implications of China’s Manufacturing Hegemony

China’s manufacturing prowess significantly shapes global supply chains, with many multinational companies relying on Chinese manufacturers for various products. This has implications for global trade balances, affecting countries differently depending on their level of integration with Chinese manufacturing. Some countries benefit from lower-priced goods, while others face challenges related to trade deficits and competition.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – a lot of future IT jobs will involve managing global supply chains, especially those originating from China. So, figuring out your career path is key, and that’s where checking out this helpful guide on choosing the right IT courses based on career goals comes in handy.
Understanding the tech behind global manufacturing, like those discussed in the China manufacturing article, will be a huge asset.
Industries heavily impacted include electronics, textiles, apparel, and consumer goods. The interconnectedness of global supply chains means disruptions in Chinese manufacturing can have ripple effects across the globe.
Technological Advancements in Chinese Manufacturing

China is actively investing in technological advancements within its manufacturing sector, aiming to move beyond low-cost manufacturing towards higher value-added production. Several Chinese companies are emerging as leaders in specific manufacturing technologies, particularly in areas like renewable energy, electric vehicles, and high-speed rail. Government initiatives and substantial funding support technological innovation and adoption.
Compared to other leading nations, China’s technological advancements in manufacturing are rapidly catching up, particularly in certain sectors. While some areas might still lag behind, the pace of innovation and investment suggests a significant narrowing of the gap in the coming years. A visual representation would show a steep upward trend for China, though still potentially below leading nations like the US, Germany, and Japan in certain advanced technologies, but closing the gap rapidly.
Concluding Remarks
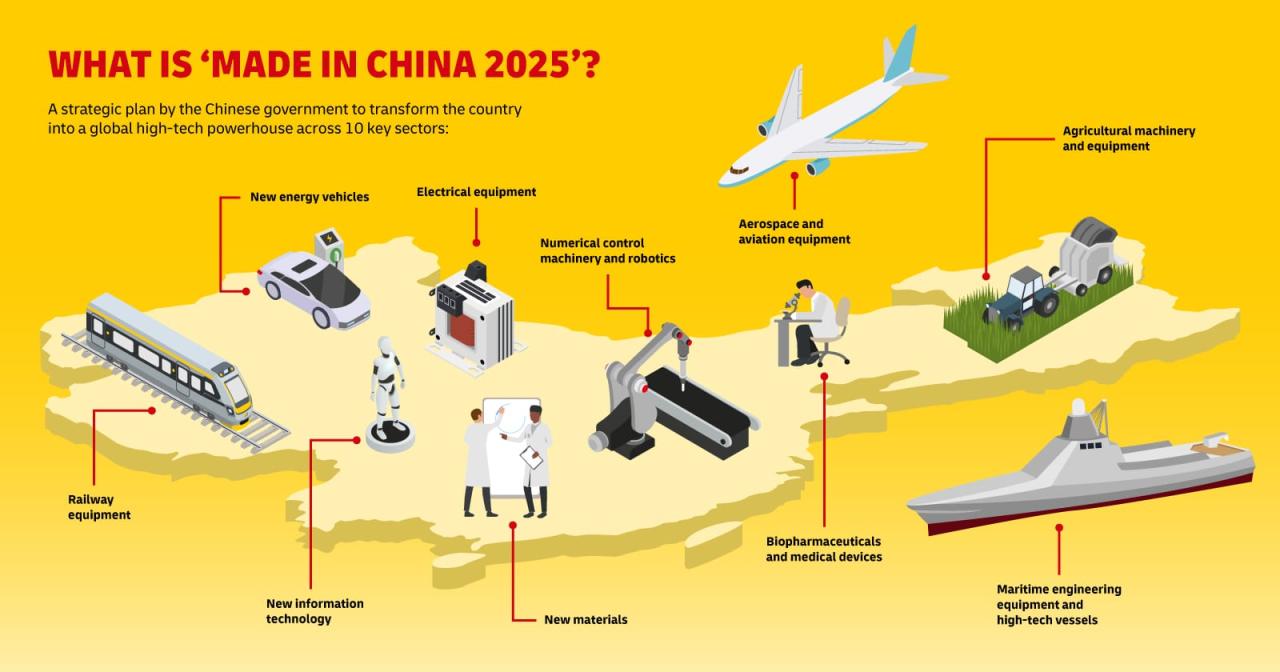
China’s manufacturing dominance is a multifaceted phenomenon with profound global implications. While its position as the world’s factory is undeniable, the future holds both opportunities and uncertainties. Understanding the factors that contributed to its rise, as well as the challenges it faces, is crucial for navigating the evolving landscape of global manufacturing and trade. The ongoing story of China’s manufacturing sector is one worth continuing to watch closely.
FAQ Resource: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News
What are some examples of specific industries where China excels in manufacturing?
China dominates in sectors like electronics, textiles, apparel, toys, and solar panels, among many others.
How does China’s manufacturing impact developing nations?
It creates both opportunities (e.g., export markets, investment) and challenges (e.g., competition, dependence on Chinese supply chains) for developing economies.
What are the environmental implications of China’s manufacturing scale?
The sheer scale of production raises significant environmental concerns, including pollution and resource depletion. China is actively working on addressing these issues, but progress is ongoing.